Endoscopy
An upper endoscopy, also called an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, is a procedure used to visually examine your upper digestive system. This is done with the help of a tiny camera on the end of a long, flexible tube. A specialist in diseases of the digestive system (gastroenterologist) uses an endoscopy to diagnose and sometimes treat conditions that affect the upper part of the digestive system.
Why it’s done ?
An upper endoscopy is used to diagnose and sometimes treat conditions that affect the upper part of the digestive system. The upper digestive system includes the esophagus, stomach and beginning of the small intestine (duodenum).
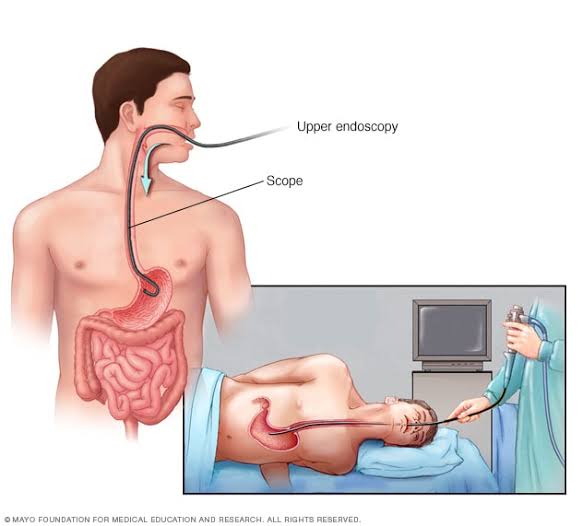
Endoscopy is recommended to:
Investigate symptoms
An endoscopy can help determine what’s causing digestive signs and symptoms, such as heartburn, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Diagnose
An endoscopy offers an opportunity to collect tissue samples (biopsy) to test for diseases and conditions that may be causing anemia, bleeding, inflammation or diarrhea. It can also detect some cancers of the upper digestive system.
Treatment
Special tools can be passed through the endoscope to treat problems in your digestive system. For example, an endoscopy can be used to burn a bleeding vessel to stop bleeding, widen a narrow esophagus, clip off a polyp or remove a foreign object.
